Backups
Most Webmin modules work by editing configuration files on your system. Each module knows which configuration files it manages, and what commands need to be run to activate them. Not all modules actually deal with config files though - for example, the Database Server modules work by executing SQL commands. As such, it cannot participate in the configuration backup process.
The Backup Configuration Files module can collect information about config files from other modules, and create and restore backups containing some or all of those files. It is designed for saving the configuration of a single system, but not for migrating configs from one server to another - that would be far more complex. You can theoretically backup the configs from one system and restore them on another if they are running the exact same OS and version (like Fedora Core 5), but attempting this between systems of different types is almost certain to fail.
How
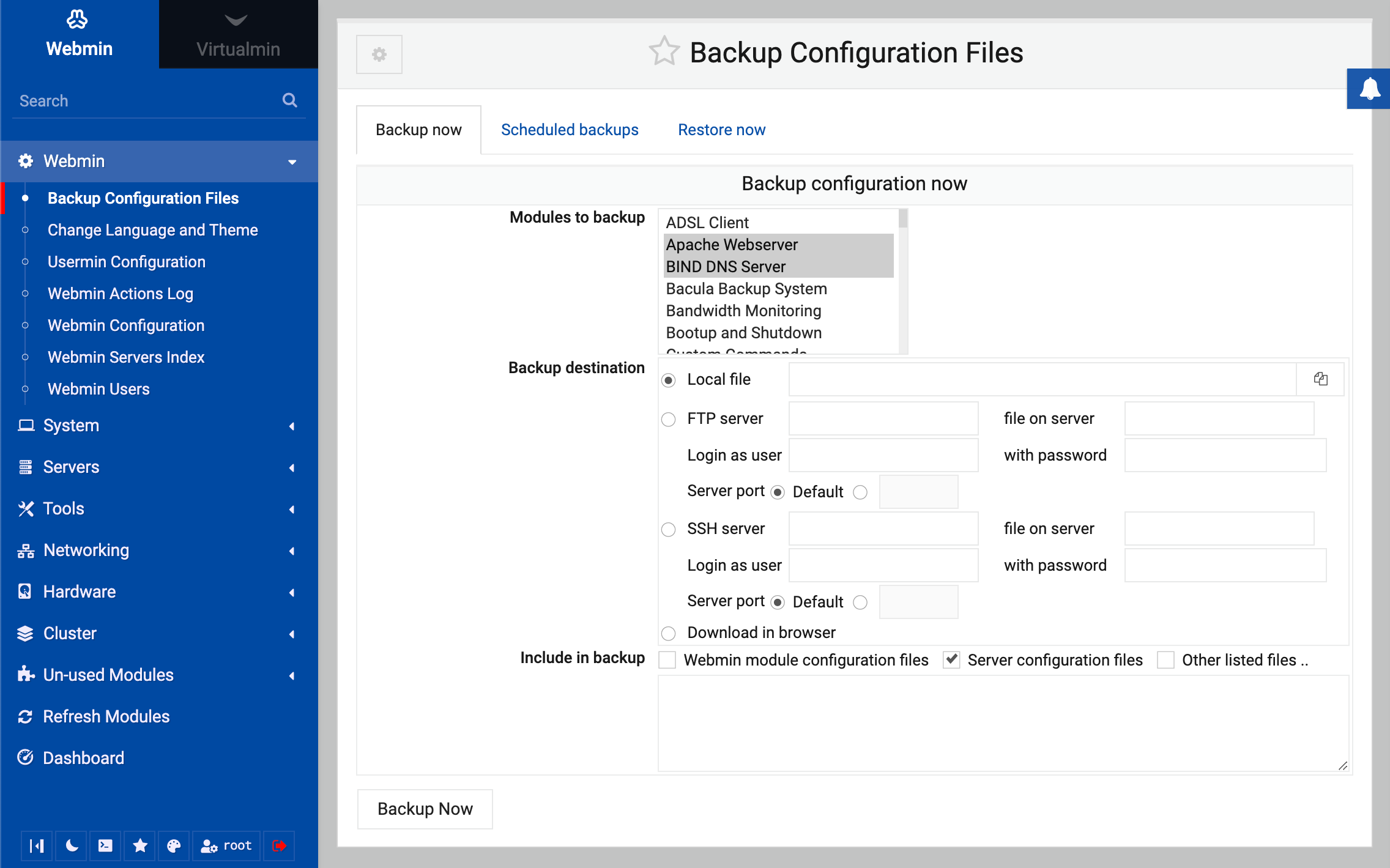
When this module (under the Webmin category) is opened, it will display a set of tabs with the form for making a backup selected by default, as in the image below.
To perform an immediate config backup, follow these steps :
- Click on the Backup now tab.
- In the Modules to backup list, select the modules you want to backup config files for, such as ‘‘Users and Groups’’. Multiple modules can be selected by ctrl-clicking.
- In the Backup destination field, select Local file and enter a path to write the backup to. This should be given a
tar.gzextension, as that is the file format used. - Click the Backup Now button.
Assuming the path you entered is valid, a page should appear showing the list of modules whose configs were backed up, and the size of the resulting file.
Backups can also be made to a remote SSH or FTP server, provided you have a login, password and writable directory. This is done by selecting the FTP server or SSH server options in step 3 above, and filling in the appropriate fields.
The “Module Config” page of this module provides options to use variables in the backup path and filename you configured. With the option for timestamp variables enabled, for example,
Scheduled backups
Once you have performed a manual backup, you can schedule it to run on a regular basis as follows :
- Click on the Scheduled backups tab.
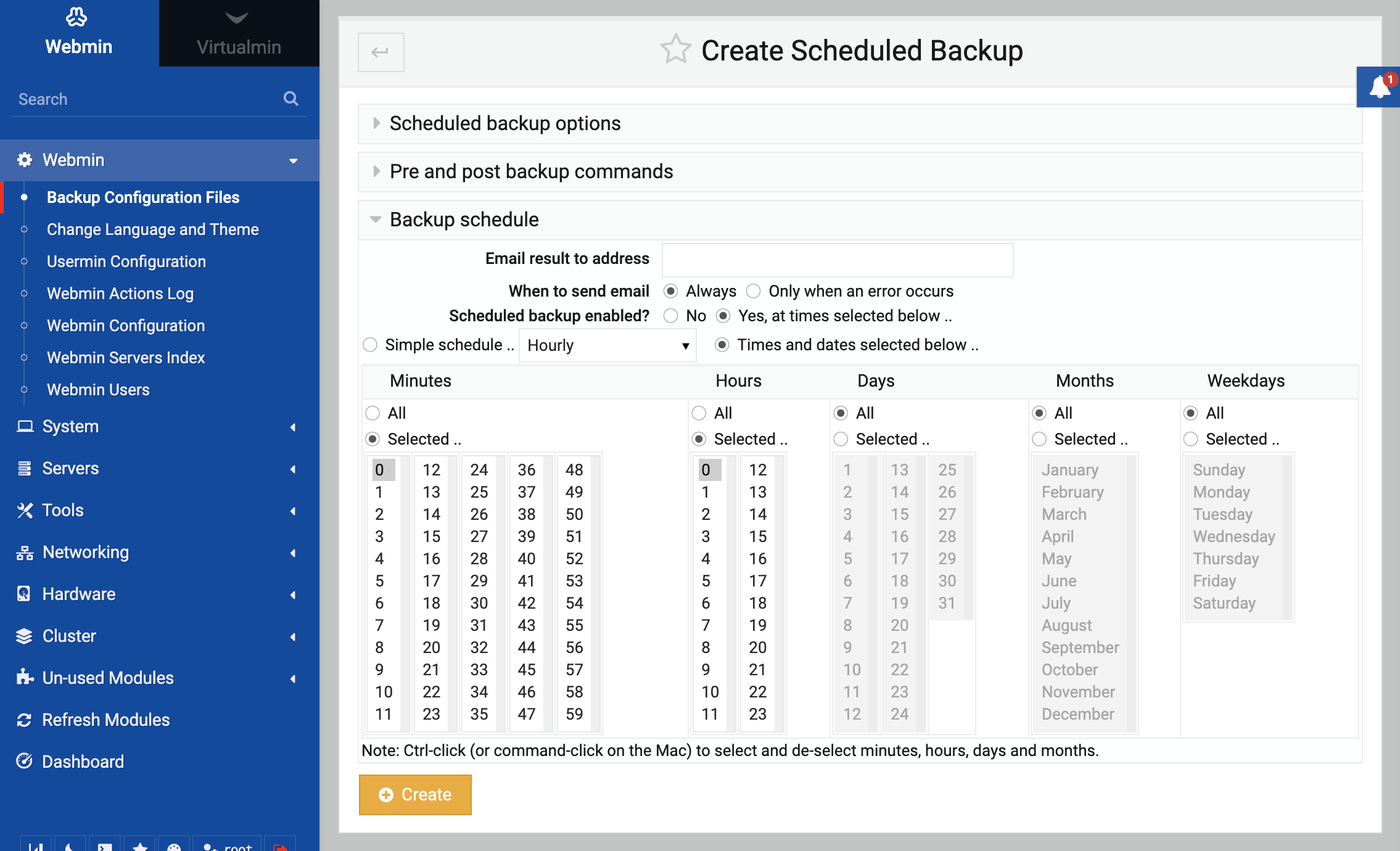
- Click the Add a new scheduled backup link, which will open the form shown below.
- Select the modules whose config files you want to include from the Modules to backup list.
- Enter a local or remote file destination in the Backup destination section.
- If you want to be notified about the status of this backup, enter your email address in the Email result to address field.
- In the Scheduled backup enabled? field select Yes, and choose the times and days for the backup to run from the Cron time selector below it.
- Click the Create button.
Once a scheduled backup has been created, you can edit or remove it by clicking on the destination path in the table under the Scheduled backups tab.
Restoring a backup
If you find that a config file on your system has been corrupted, incorrectly edited or mistakenly deleted, it can be easily restored using this module. The steps to perform a restore are :
- Click on the Restore now tab.
- Select the module or modules whose config files you want to restore from the Modules to restore menu.
- In the Restore from section, enter the path to a local or remote file that was originally created by this module. To be useful, it must contain backups for the modules that you selected above.
- Click the Restore Now button.
If all goes well, a page will be displayed showing the number of modules and files restored. Files will be restored to their original locations on the system, rather than the paths that are set on the Module Config pages of the selected modules.